User authentication is made possible by a digital certificate. Third-party authentication makes use of certificates in place of requiring each user to be authenticated by every participant in an application.
What is a digital certificate?
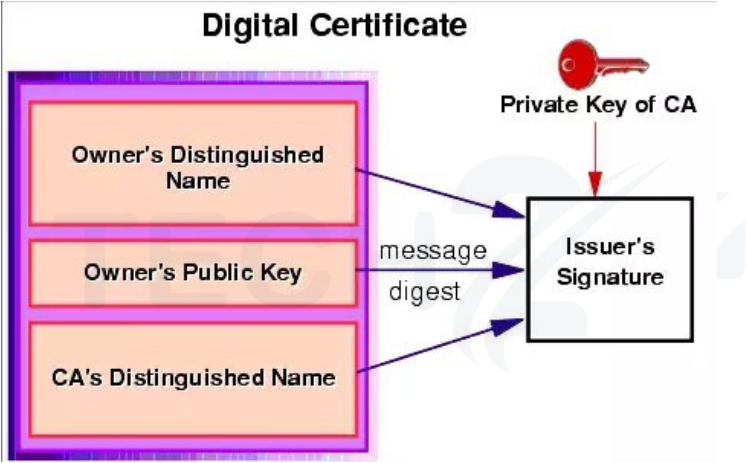
The ownership of a public key is linked cryptographically to the entity that owns it using a digital certificate, which is also referred to as a public key certificate. Public keys used for authentication and encryption are shared through digital certificates. The main purposes of the public key infrastructure (PKI), which is the mechanism for distributing and authenticating public keys, are the distribution, authentication, and revocation of digital certificates.
Key pairs are the foundation of public key cryptography; one private key is kept secret by the owner and is used for signing and decrypting, while the other is a public key that may be used to encrypt data given to the owner of the public key or to verify the authenticity of the data signed by the certificate holder. Entities can exchange their public key for authentication purposes thanks to the digital certificate. The most popular application of digital certificates in public key cryptography is to launch Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connections across web browsers and websites.
A like blog – Janitor ai
How do you use digital certificates?
The following applications for digital certificates:
- To verify that the transactions are safe and genuine, debit and credit cards with integrated chips communicate with retailers and banks.
- A central server in the data center is used by digital payment businesses to authenticate their self-service teller machines, kiosks, and point-of-sale equipment in the field.
- Digital certificates can be used for digital document signing as well as user identification in secure email. Emails are digitally signed by the sender and verified by the recipient.
- Manufacturers of computer hardware incorporate digital certificates into cable internet connections to assist in stopping broadband service theft caused by device cloning.
Who is authorized to issue digital certificates?
A self-signed certificate can be made by an entity by developing its own PKI and issuing its own digital certificates. When a company manages its own PKI to issue certificates for internal usage, this strategy can make sense. However, the majority of digital certificates are issued by certificate authorities (CAs), which are regarded as trusted third parties in the terms of a PKI. People can extend their faith in the CA to the digital certificates it issues by using a reliable third party to issue digital certificates.
Benefits of digital certificates
The following advantages are offered by digital certificates:
- Privacy: Digital certificates protect sensitive data when you encrypt communications and stop anyone who isn’t supposed to see it from seeing it. This technology safeguards organizations and people who handle vast amounts of private information.
- Ease of use: The majority of the digital certification procedure is automated.
- Monetary efficiency: Digital certificates are more affordable when compared to other encryption and certifying methods. Most digital certificates have an annual cost of less than $100.
- Flexibility: Digital certificates can be obtained without going via a CA. It is possible to create digital certificates on your own for enterprises that are interested in setting up and managing their own private pool.

What kinds of digital certificates are there?
Three different types of digital certificates are used by web servers and browsers to authenticate online. The following are the three categories:
- Domain-validated (DV): SSL certificates with domain validation (DV) provide the least amount of confidence in the certificate’s holder. Applications for DV SSL certificates simply require proof of domain name usage authorization.
- Organization-validated (OV): Additional guarantees concerning the certificate holder are offered by organization-validated (OV) SSL certificates. They attest to the applicant’s legitimacy in using the domain.
- Extended validation (EV): SSL certificates with extended validation (EV) are only issued when the applicant satisfies the CA as to their identity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Digital certificates safeguard data and interactions, frequently between websites and browsers, in a similar manner to passwords. By informing the browser that a connection and the transfer of information are secure, they can be used to authenticate a website.
A like blog – GEOMETRIC DEEP LEARNING
